Understanding currency pair correlations is a critical skill for any forex trader. Currency correlations measure the relationship between the movements of two currency pairs, allowing traders to identify potential opportunities, manage risk, and make informed decisions. A positive correlation means two currency pairs move in the same direction, while a negative correlation indicates they move in opposite directions.
Dollar is the counter currency in both pairs. Conversely, USD/JPY and EUR/USD may exhibit a negative correlation as the dollar plays different roles in these pairs. By analyzing these relationships, traders can avoid overexposing themselves to risk by trading highly correlated pairs or capitalize on diversification by balancing positively and negatively correlated pairs in their portfolios.
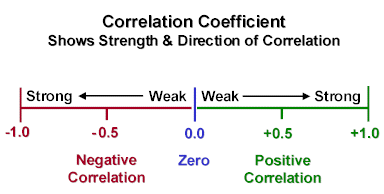
To leverage currency pair correlations effectively, traders should monitor correlation coefficients, typically ranging from -1 to +1. A coefficient close to +1 indicates a strong positive correlation, while one near -1 suggests a strong negative correlation. Tools like correlation matrices and real-time data from trading platforms can help in evaluating these metrics.
Incorporating currency correlations into your strategy requires practice and awareness. When used wisely, they can enhance your trading decisions, improve portfolio management, and mitigate risks associated with unforeseen market volatility. Understanding and utilizing this powerful concept can give
Currency Pair Correlations: How to Use Them to Your Advantage
In the world of forex trading, understanding currency pair correlations can significantly enhance your trading strategyThis relationship can help traders identify opportunities, manage risk, and build more robust trading portfolios.
What Are Currency Pair Correlations?
Currency pair correlations measure how two currency pairs move in relation to each other. Dollar serves different roles in these pairs.
Benefits of Understanding Correlations
- Risk Management
By , correlations, traders can avoid overexposing themselves to similar market risks. Trading two highly correlated pairs, such as EUR/USD and GBP/USD, effectively doubles your exposure to the U.S. dollar, increasing your risk. - Diversification
This approach spreads risk and reduces the impact of adverse market movements on your overall trades. - Enhanced Decision-Making
Understanding correlations helps traders anticipate potential price movements. If one pair begins trending strongly, a correlated pair may follow, providing additional opportunities for profit.
Using Correlation Coefficients
Correlation coefficients are numerical values between -1 and +1 that indicate the strength of the relationship between two currency pairs:
- -1: Perfect negative correlation (both pairs move in opposite directions).
- 0: No correlation (pairs move independently of each other).
These coefficients can be analyzed using correlation matrices, which are often available on trading platforms. Reviewing these metrics regularly is crucial, as correlations can change over time due to economic events, geopolitical factors, or market sentiment.
Practical Application in Trading
To use correlations to your advantage:
- Avoid Overexposure: Limit trading on multiple highly correlated pairs to prevent amplifying risks.
- Hedge Positions: Use negatively correlated pairs to hedge against potential losses.
- Confirm Trends: Use correlated pairs to validate your analysis. For example, if EUR/USD and GBP/USD are both trending upwards, it reinforces the strength of a bullish trend.
Currency pair correlations are a valuable tool in forex trading, offering insights into how different currency pairs move relative to one another.This article delves into the concept of currency pair correlations and how to use them effectively in your trading strategy.
- What Are Currency Pair Correlations?
Currency pair correlation measures the statistical relationship between two currency pairs, indicating whether they move in the same direction, opposite directions, or independently of each other.
- For instance, USD/JPY and EUR/USD typically have a negative correlation.
- No Correlation: When there’s no discernible relationship between two pairs.
Correlation Coefficient:
- +1: Perfect positive correlation.
- -1: Perfect negative correlation.
- 0: No correlation.
- Why Do Currency Pairs Correlate?
Several factors contribute to currency pair correlations, including:
- Economic Ties
Countries with strong trade or economic relationships often see their currencies move in tandem. For example, the euro (EUR) and British pound (GBP) are influenced by the European Union’s economic activities.
- Shared Base or Quote Currencies
Pairs sharing a common currency tend to correlate. For instance, EUR/USD and USD/JPY involve the U.S. dollar, linking their movements indirectly.
- Commodity Dependencies
Currencies tied to commodity exports (e.g., AUD, CAD, NZD) often move similarly when commodity prices fluctuate.
- Global Sentiment
Risk-on and risk-off sentiment influence correlations. Safe-haven currencies like USD and JPY behave oppositely to riskier assets like AUD and NZD during market turbulence.
- How to Measure Correlation
Forex traders use correlation coefficients to quantify the strength and direction of relationships between pairs. These values are typically calculated over specific timeframes, such as daily, weekly, or monthly.
Correlation Table
Many trading platforms and websites provide correlation tables showing the relationships between major currency pairs.
- Strong Positive: Values closer to +1 (e.g., EUR/USD and GBP/USD).
- Strong Negative: Values closer to -1 (e.g., EUR/USD and USD/CHF).
- Weak or No Correlation: Values near 0.
- How to Use Currency Correlations in Trading
- Diversification
Traders can use correlations to diversify their portfolios and reduce risk exposure. Avoid overloading your positions with highly correlated pairs, as this amplifies risk. Instead, include pairs with weak or negative correlations for better balance.
Example:
- If you’re long on EUR/USD, avoid also going long on GBP/USD, as their strong positive correlation may double your exposure.
- Instead, consider pairing EUR/USD with USD/JPY for a balanced approach.
- Risk Management
Correlation analysis helps in managing risks associated with market movements.
- Hedging: Use negatively correlated pairs to hedge your positions. For instance, if you’re long on EUR/USD, a short position on USD/CHF can offset potential losses.
- Identifying Opportunities
Discrepancies in correlated pairs can signal trading opportunities. If EUR/USD rises but GBP/USD lags, the latter might catch up, presenting a potential entry point.
- Avoiding Overexposure
Trading multiple highly correlated pairs can inadvertently increase leverage and risk. Monitor correlations to ensure you’re not overly exposed to a single market trend.
- Practical Example of Correlation in Action
Suppose you notice the following correlations:
- EUR/USD and GBP/USD: +0.85 (strong positive correlation).
- USD/JPY and AUD/USD: -0.75 (strong negative correlation).
Scenario:
- You anticipate a bullish trend for the U.S. dollar.
- Based on the correlation, you could:
- Short EUR/USD (a dollar-positive move).
- Avoid GBP/USD to reduce overexposure.
- Long USD/JPY for added diversification.
This approach balances risk and aligns with your market outlook.
- Tools for Analyzing Correlations
- Trading Platforms
Platforms like MetaTrader 4/5 or cTrader often have built-in correlation tools.
- Online Resources
Websites such as Myfxbook and OANDA provide up-to-date correlation tables and calculators.
- Excel or Python
For custom analysis, you can calculate correlations using Excel or programming languages like Python, using historical price data.
- Indicators
Some traders use correlation indicators directly on their charts to visualize relationships in real-time.
- Limitations of Correlations
While useful, currency correlations have limitations:
- Dynamic Nature
Correlations change over time due to shifting market conditions, economic policies, or geopolitical events. A strong correlation today might weaken tomorrow.
- False Signals
Overreliance on correlations can lead to false signals, especially during periods of high volatility or unexpected news events.
- Dependency on Timeframes
Correlations vary across different timeframes. A strong correlation on a daily chart might not hold on a monthly chart.
- External Factors
Central bank interventions, political events, or natural disasters can disrupt correlations unexpectedly.
- Tips for Effective Use of Correlations
- Monitor Regularly: Reassess correlations periodically to account for market changes.
- Combine with Other Analysis: Use correlations alongside technical and fundamental analysis for well-rounded decisions.
- Start Small: Practice with a demo account to understand how correlations affect your trades.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Always protect your positions against unexpected market movements.